In this lab, we tested how
proteins are produced by our body. First, a copy of a
DNA gene, called Messenger
RNA, goes to the cytoplasm. Next, the mRNA bonds to a
ribosome. The
ribosome reads the mRNA as a codon, three bases at a time and adds an
amino acid to a chain. Amino acids bond together to make the primary structure of a protein The chain twists and turns to form a protein.
 |
| Protein Synthesis |
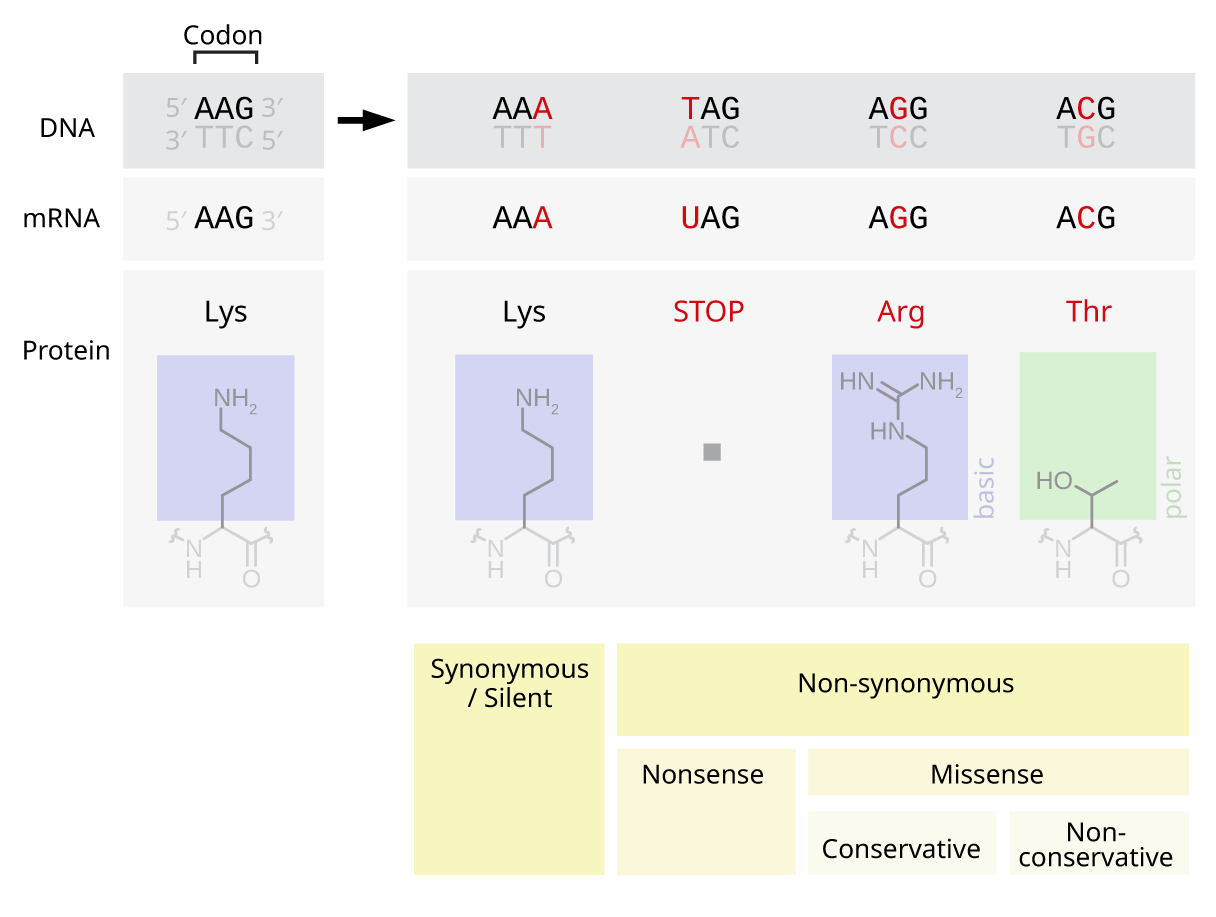
The effects of
mutations on proteins can range from none to very severe. A
substitution seemed to have the least affect. In our case, it did not effect the protein
sequence. The worst it could do was changing one protein of the sequence.The next worst
mutation was
insertion. When an extra base was inserted into the
DNA, the protein changed dramatically. Every protein after the mutation was different than the original protein chain. The proteins before the mutation stayed the same. The mutation with the greatest effect was the
deletion. It completely changed the structure of the protein. It coded for different proteins than the original strand after the second protein. After the fourth protein, there was a stop codon, meaning to stop translating. The resulting
sequence was only four proteins long. There is an effect on where the mutation is placed. For substitution, it does not matter where the mutation is. For
insertions and
deletions, the closer the mutation is to the beginning of the gene, the more damage the mutation will do.
 |
| Mutations |
When I got to choose my own mutation, I decided to use a deletion. I used a deletion because it had the greatest effect on the protein in the previous problems. I decided to put my mutation at the very front. The first letter of the amino acid chain was changed. The result was a completely different protein. It had the greatest effect out of all the other mutations. I chose to put the mutation in the very front to maximize the power of it. Since the mutation was in the very front, everything was changed.
 |
My mutation
|
There are many different types of genetic disorders caused by mutations. An example is Tay-Sachs disease. Mutations in the
Hexa gene, which provides instructions for making
beta-hexosaminidase A, an enzyme responsible for critical functions in the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms of the disease include loss of motor skills, vision and hearing loss, and paralysis. Although the disease is not very common, there are still people who have it. It shows the power of mutations.
 |
| Gene whose mutations cause Tay-Sachs disease |



No comments:
Post a Comment