Whew! This year has gone by so fast. Biology has been so much fun. I am a little bit sad that this will be last blog post of the year. It will be about Unit 10, anatomy and physiology.
We first learned about the all important concept of homeostasis. There are two types of feedback loops, negative and positive. They involve changing your behavior based on feedback from the environment. Negative feedback loops involve "dancing" around a set point. Positive feedback loops involve going away from a certain point. Behavioral responses are responses from the whole of the organism. These include hibernation and migration. Physiological responses involve just part of the body. Some examples of maintaining homeostasis are the blood glucose cycle and thermoregulation.
The next topic we learned about was the circulatory and respiratory system. We learned these two topics together because they are interconnected. The circulatory system transports blood, gasses, and nutrients.They separate oxygen poor and oxygen rich blood. The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs with the circulatory system. Breathing involves the diaphragm and the muscles of the rib cage. Air flows from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, tiny air sacs of the lungs. Oxygen diffuses into the capillaries ad binds to hemoglobin in the red blood cells. Carbon dioxide diffuses from capillaries into alveoli.
The heart has four chambers, 2 atria and 2 ventricles. Valves in each of the chambers prevent back flow. We learned a simplified version of the heart called the "box" heart
Oxygen poor blood enters the right atrium then the right ventricle pours blood to the lungs. Oxygen rich blood from the lungs enters the left atrium, then the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps blood to the body. The heart beat consists of two contractions. The SA node, the pacemaker, stimulates atria to contract. The AV node stimulates ventricles to contract. The "lub" happens when the tricuspid and the bicuspid (AV) valves during ventricle contractions. The "dub" happens when the quartic and pulmonary (SV) valves close when the heart releases.
The heart pumps blood through two main pathways. Pulmonary circulation occurs between the heart and the lungs. It removes carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen. The systemic circulation occurs between the heart and the rest of the body. Oxygen rich blood goes to the organs. Oxygen poor blood returns to the heart.
Blood pressure is a measure of force of blood pushing against artery walls. Systolic pressure occurs when the left ventricle contracts. Diastolic blood pressure occurs when the ventricle relaxes. The formula to calculate blood pressure is Systolic/ Diastolic. High blood pressure can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Arteries, veins, and capillaries transport blood to all parts of the body. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Blood is under greater pressure and arteries are more thicker and muscular. Veins carry blood back to the heart. The blood is under less pressure. The wall are thinner and have a larger diameter.
Lifestyle plays an important part in circulatory disease. Factors such as smoking, lack of exercise, and excessive weight lead to increased risk of circulatory disease.
Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells make up around 45% of all blood. They transport oxygen and carry away carbon dioxide. They have no nuclei and contain hemoglobin. White blood cells help fight pathogens and destroy foreign matter. Platelets help form clumps that control bleeding.
Next is the nervous system. There are two parts of the nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain, the brainstem, and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes the cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and the sensory and motor neurons. They pass signals between one another. The brain has four parts that control different things. The cerebrum controls thought, movement, and motion. The diencephalon, the interbrain, coordinates the endocrine system, sorts and directs into the cerebrum. The cerebellum involves the subconscious, calculates force and direction of muscle contractions, and determines body position. The brain stem controls basic life functions like reflexes, breathing, heart function, swallowing, and coughing. The spinal cord controls reflexes. The sensory neuron sends impulses to the spinal cord. The spinal cord directs impulses to motor neurons and does not involve the brain.
Neurons have three parts. The cell body as a nucleus and organelles. Dendrites receive impulses. The axon carries impulses. Neurons have schwann cells, synapses, and terminals to transmit signals. Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from sensory receptors in the body. The association neurons carry impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons. Motor neurons carry nerve impulses from ends to muscles and glands. Stimulus starts the action potential at the dendrite. The stimulus travels the length of the neuron to the axon terminal. The chemical signal passes between neurons. Neurotransmitters are used in different parts of the brain for different purposes.
Next, we move on to the endocrine system. The endocrine system is a system of glands that release hormones. The nervous system is used for short term fast communication, while the endocrine system is slower and has a more lasting effect. A hormone is produced by a gland and travels through the circulatory system. Hormones when released stimulate other glands to produce hormones. There are many examples of hormones. The hypothalamus links the nervous system to the pituitary gland to control body temperature, blood pressure, and various other functions. The pituitary gland gets instructions from the hypothalamus telling it what hormones to produce so that it can control other endocrine glands. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine that controls the growth and structure of bone, puberty, and metabolism. The parathyroid gland releases hormone that regulate calcium levels. The adrenal gland releases the "fight or flight" hormone called epinephrine and the stress hormone called cortisol. Adrenaline is a hormone that increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar,and blood flow. Cortisol increases blood sugar, suppresses the immune system, and aids in metabolism of carbs, fats, and proteins. The pancreas is a gland that releases insulin and glucagon. Insulin decreases blood sugar levels. Glucagon increases them.
The next very important system we learned about is the digestive system. We first learned about that many nutrients that are body needs. Water makes up 55-60% of our bodies. It is involved in almost every cellular processes. Carbohydrates are our main source of energy. Fats provide energy and are a key building component. Proteins are necessary for growth and repair of the body's cells. Minerals are inorganic materials that are essential to cellular function. Vitamins are organic molecules that work with enzymes.
There are two types of digestion: mechanical and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion involves the breaking of food by using contractions of the muscle. Chemical digestion involves the breaking of food using enzymes and extreme pH. Many organs work together to break down food. Digestion begins in the mouth and continues in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine.
Most nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine. The folded lining, villi, and microvilli help absorb nutrients. Water is absorbed in the large intestine. Undigested material forms solid feces that is stored in the rectum and eliminated through the bladder.
There is whole ecosystem of bacteria in the gut flora. The bacteria help synthesize important vitamins, help with absorption, and ferment indigestible foods. A poor diet can kill these good bacteria, which can lead to health problems,
Another important organ system we learned about is the immune system. First we learned about the different types of pathogens. They include bacteria, fungi, viruses, and pathogens. The immune system has two parts: the nonspecific and the adaptive responses. The nonspecific defenses are the same for every pathogen. These include the skin, mucus, and low pH. Phagocytes work by swallowing pathogens. Natural killer cells kill pathogens by releasing cytokines that cause a cell to lysis. Adaptive immunity is only in vertebrates. It relies on the recognition of specific traits such as antigen receptors. There are two types of immune responses. They are the humoral response and the cell mediated response.
The last vodcast we had was about the lymphatic system. It is a system of tubes and sacs in the body. The lymphatic system cleans waste from the body. It includes white blood cells that engulf pathogens and mast cells that release histamine. The inflammatory response is your body responding to a pathogen. There are many types of inflammatory responses. Acute local infection is when a pathogen enters the body at a specific spot. A systemic inflammation is when the body is under attack throughout the body. Pimples are part of the body's localized response to bacteria that got stuck in pus.
The small intestine is where the front lines of the immune system lie. As food is absorbed through the gut, pathogens try to hide. Immune cells capture foreign invaders and kill them. Leaky gut syndrome occurs when the intestinal walls become irritated and let in food and pathogens. Chronic systemic inflammation is when the body is constantly fighting off foreign substances. Some foods can cause inflammation. These can include gluten and lactose. Everyone has various levels of sensitivity.
I still want to learn more about some systems that were not covered, such as the excretory system. I also want to learn more about the nervous system. The brain is very interesting and complex, and I want to learn more about it.
This is my last post of the year. I have grow a lot since the beginning of freshman year of SHS. I have learned better study skills and time management skills. I know a lot more people and am not afraid to try new things. I have joined many clubs that suit my interests, such as the Environmental club and the History club. Additionally, I have learned a lot more biology. I am excited to take Chemistry Honors next year.
Some of my favorite posts this year have been
1.) 20 Questions in Science
2.) Genetics Infographic
3.) 20 Time
I have really enjoyed biology this year. Thanks for taking the time to read my blog.
We first learned about the all important concept of homeostasis. There are two types of feedback loops, negative and positive. They involve changing your behavior based on feedback from the environment. Negative feedback loops involve "dancing" around a set point. Positive feedback loops involve going away from a certain point. Behavioral responses are responses from the whole of the organism. These include hibernation and migration. Physiological responses involve just part of the body. Some examples of maintaining homeostasis are the blood glucose cycle and thermoregulation.
 |
| Thermoregulation |
 |
| Gas exchange |
The heart has four chambers, 2 atria and 2 ventricles. Valves in each of the chambers prevent back flow. We learned a simplified version of the heart called the "box" heart
 |
| The "Box" Heart |
Oxygen poor blood enters the right atrium then the right ventricle pours blood to the lungs. Oxygen rich blood from the lungs enters the left atrium, then the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps blood to the body. The heart beat consists of two contractions. The SA node, the pacemaker, stimulates atria to contract. The AV node stimulates ventricles to contract. The "lub" happens when the tricuspid and the bicuspid (AV) valves during ventricle contractions. The "dub" happens when the quartic and pulmonary (SV) valves close when the heart releases.
The heart pumps blood through two main pathways. Pulmonary circulation occurs between the heart and the lungs. It removes carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen. The systemic circulation occurs between the heart and the rest of the body. Oxygen rich blood goes to the organs. Oxygen poor blood returns to the heart.
Blood pressure is a measure of force of blood pushing against artery walls. Systolic pressure occurs when the left ventricle contracts. Diastolic blood pressure occurs when the ventricle relaxes. The formula to calculate blood pressure is Systolic/ Diastolic. High blood pressure can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Arteries, veins, and capillaries transport blood to all parts of the body. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Blood is under greater pressure and arteries are more thicker and muscular. Veins carry blood back to the heart. The blood is under less pressure. The wall are thinner and have a larger diameter.
Lifestyle plays an important part in circulatory disease. Factors such as smoking, lack of exercise, and excessive weight lead to increased risk of circulatory disease.
 |
| Blood |
Next is the nervous system. There are two parts of the nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain, the brainstem, and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes the cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and the sensory and motor neurons. They pass signals between one another. The brain has four parts that control different things. The cerebrum controls thought, movement, and motion. The diencephalon, the interbrain, coordinates the endocrine system, sorts and directs into the cerebrum. The cerebellum involves the subconscious, calculates force and direction of muscle contractions, and determines body position. The brain stem controls basic life functions like reflexes, breathing, heart function, swallowing, and coughing. The spinal cord controls reflexes. The sensory neuron sends impulses to the spinal cord. The spinal cord directs impulses to motor neurons and does not involve the brain.
Neurons have three parts. The cell body as a nucleus and organelles. Dendrites receive impulses. The axon carries impulses. Neurons have schwann cells, synapses, and terminals to transmit signals. Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from sensory receptors in the body. The association neurons carry impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons. Motor neurons carry nerve impulses from ends to muscles and glands. Stimulus starts the action potential at the dendrite. The stimulus travels the length of the neuron to the axon terminal. The chemical signal passes between neurons. Neurotransmitters are used in different parts of the brain for different purposes.
 |
| A neuron |
 |
| Endocrine glands |
The next very important system we learned about is the digestive system. We first learned about that many nutrients that are body needs. Water makes up 55-60% of our bodies. It is involved in almost every cellular processes. Carbohydrates are our main source of energy. Fats provide energy and are a key building component. Proteins are necessary for growth and repair of the body's cells. Minerals are inorganic materials that are essential to cellular function. Vitamins are organic molecules that work with enzymes.
There are two types of digestion: mechanical and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion involves the breaking of food by using contractions of the muscle. Chemical digestion involves the breaking of food using enzymes and extreme pH. Many organs work together to break down food. Digestion begins in the mouth and continues in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine.
 |
| Digestive System |
There is whole ecosystem of bacteria in the gut flora. The bacteria help synthesize important vitamins, help with absorption, and ferment indigestible foods. A poor diet can kill these good bacteria, which can lead to health problems,
Another important organ system we learned about is the immune system. First we learned about the different types of pathogens. They include bacteria, fungi, viruses, and pathogens. The immune system has two parts: the nonspecific and the adaptive responses. The nonspecific defenses are the same for every pathogen. These include the skin, mucus, and low pH. Phagocytes work by swallowing pathogens. Natural killer cells kill pathogens by releasing cytokines that cause a cell to lysis. Adaptive immunity is only in vertebrates. It relies on the recognition of specific traits such as antigen receptors. There are two types of immune responses. They are the humoral response and the cell mediated response.
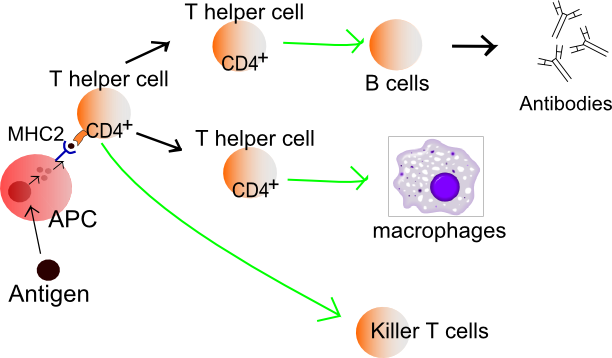 |
| The immune system |
The last vodcast we had was about the lymphatic system. It is a system of tubes and sacs in the body. The lymphatic system cleans waste from the body. It includes white blood cells that engulf pathogens and mast cells that release histamine. The inflammatory response is your body responding to a pathogen. There are many types of inflammatory responses. Acute local infection is when a pathogen enters the body at a specific spot. A systemic inflammation is when the body is under attack throughout the body. Pimples are part of the body's localized response to bacteria that got stuck in pus.
The small intestine is where the front lines of the immune system lie. As food is absorbed through the gut, pathogens try to hide. Immune cells capture foreign invaders and kill them. Leaky gut syndrome occurs when the intestinal walls become irritated and let in food and pathogens. Chronic systemic inflammation is when the body is constantly fighting off foreign substances. Some foods can cause inflammation. These can include gluten and lactose. Everyone has various levels of sensitivity.
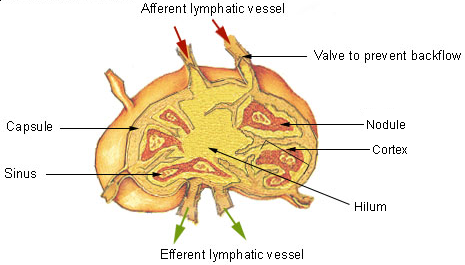 |
| Lymphatic system |
This is my last post of the year. I have grow a lot since the beginning of freshman year of SHS. I have learned better study skills and time management skills. I know a lot more people and am not afraid to try new things. I have joined many clubs that suit my interests, such as the Environmental club and the History club. Additionally, I have learned a lot more biology. I am excited to take Chemistry Honors next year.
Some of my favorite posts this year have been
1.) 20 Questions in Science
2.) Genetics Infographic
3.) 20 Time
I have really enjoyed biology this year. Thanks for taking the time to read my blog.