 |
| A phylogenetic tree |
In this unit, we learned about how organisms are classified and what on earth evolved. Organisms are classified by how similar they are. Taxonomy is the study of naming and classifying organisms. Carrolus Linneaus, a Swedish botanist came up with this system. He used a system known as binomial nomenclature. The first part of the name is capitalized an it is the genus. The second part the species name. They are usually in latin or greek and must be italicized or underlined. Phylogeny shows evolutionary relationships using taxonomy. The taxonamic levels are ordered from most inclusive to least inclusive. It goes from Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species.
However, there was need for a more inclusive taxonomical level. This led to the creation of the domain. Originally, Linnaeus only knew about plants and animals. The invention of the microscope led to scientists discovering bacteria. This led to two domains: Bacteria and Eukarya. Scientists however discovered that there was a "new" form of bacteria that was chemically and genetically different. They named it Archea, and thus the 3 domain system began.
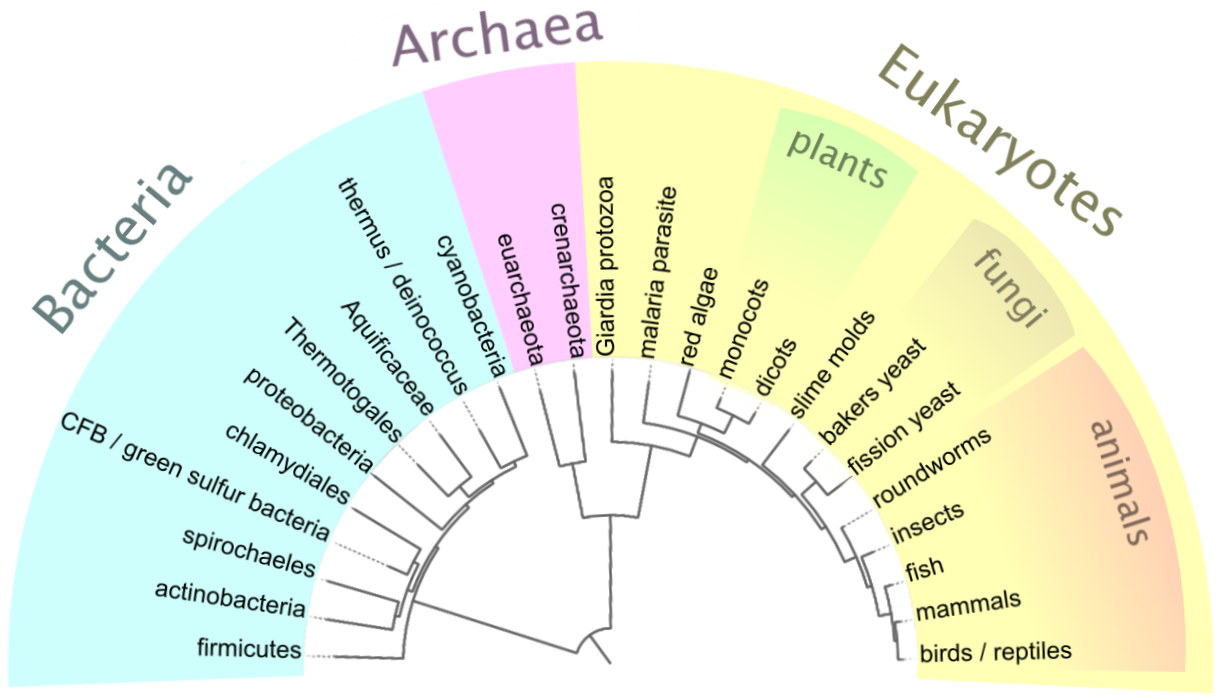 |
| The Three domains |
 |
| Bacteria |
Bacteria were likely Earth's first organism. They are unicellular and come in three shapes: spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals. They are further divided into gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Gram positive bacteria have a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan, while Gram negative bacteria have less peptidoglycan, an outer membrane that can be toxic, and can be antibiotic resistant, Scientists use a gram stain to tell the difference. Most mobile bacteria have a flagella, a whip like structure in order to move. Bacteria metabolize in many ways. Chemoheterotrophs are heterotrophic bacteria that take in organic molecules. Photoautotrohps use light to convert CO2 and H2O into glucose through photosynthesis. Chemoautrotrophs use energy directly from chemical reactions. Obligate aerobes must have oxygen in order to survive. Obligate anerobes can not have oxygen. Faculative anerobes alternate between fermentation and oxygen depending on the environment. Bacteria work as decomposers, as symbiosis, and in biotechnology.
Viruses are very interesting. They are not considered life and are not cells. They are very small infectious particles that consist of a nucleic acid in a protein coat. Capsids in the protein coat enclose the viral genome. They help the virus infect host cells. Once a virus infects a host cell, it begins to manufacture its own proteins by using the host cells ribosomes. There are two types of infections. Lytic infections are when a virus enters a cell, makes copies of itself, and causes the cell to burst. Lysogenic infections are when a virus integrates its DNA into the DNA of the host cell, and the viral genetic information replicates along with the host cell's DNA. Retroviruses use reverse transciptase to copy their RNA genome into DNA. HIV( Human Immunodeficiency Virus), is the retroviruses that causes AIDS (Aquired Immunodeficiency Virus). Viruses kill cells by releasing hydrolite enzymes from lysosomes.
 |
| Ebola Virus |
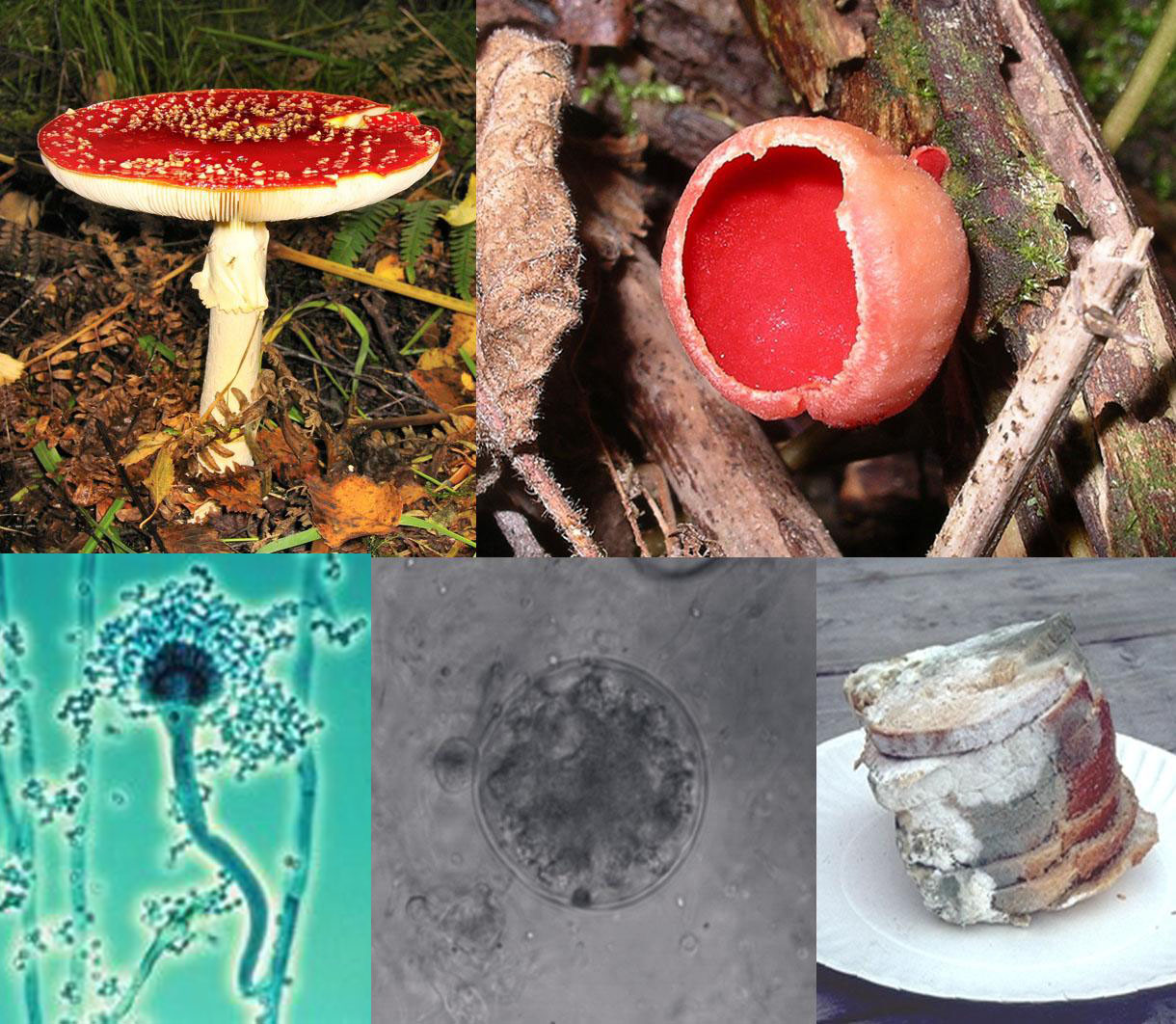 |
| A collage of fungi |
Fungi have cell walls made up of chitin. They are multicellular, with the exception of yeast. There are three types of fungi. Sac fungi form a reproductive sac, or ascus. Bread molds are kind of the misfits. Club fungi have fruiting bodies that are club shaped. Multicellular fungi have a complex reproductive cycle that includes either sexual or asexual reproduction, or both. Fungi act as mutualism. They are useful in several ways. They make foods, they work as antibiotics, and are model systems for molecular biology. However, they also cause disease.
The first plants grew at the edges of the water. They have a cuticle, a waxy protective layer, to survive drying out. They also have a vascular system that allows them to move resources to different parts. They have pollen grains to allow for reproduction without free standing water, a seed, and a fruit. Bryophyta are mosses. They are the most common seedless nonvascular plants. Pterophyta (ferns) are seedless vascular plants. A vascular system allows them to get more water off the ground, resulting in more photosynthesis. Roots allow the absorption of more water and nutrients. Leaves allow for more photosynthesis. Gymnosperms are cone bearing plants. The cone is the reproductive structure of most gymnosperms. Pollen is produced in the male. cone. Seeds are produced in the female cones. The major phyla are cycloids, ginkos, and conifers. .Angiosperms are flowering plants. They are the dominant species of plants alive today. They have a flower, their reproductive organ, to allow for more efficient pollination. A fruit is a mature ovary, which allows for efficient seed dispersal. There are two major types of angiosperms. Monocots have a single seed lead, their leaf veins are usually parallel, flower parts come in multiples of 3, and have bundles of vascular tissue scattered in the stem. Dicots have two seed leaves, their leaf veins are usually net like, flower parts are usually in multiples of three or four, and have bundles of vascular tissue in rings in the stem.
 |
| Flowers! |
 |
| Invertebrates |
Invertebrates are a very diverse class. They are diploid and usually reproduce sexually. Most animals are invertebrates. Sponges (phylum poriferia) are the most primitive animals. They have specialized cells but no tissues. They are sessile and have no symmety. They can reproduce both sexually and asexually, and their cells work together to filter feed. Cnidarians are the oldest existing animal group that have specialized tissues. They have 2 body forms, polyps and medusas. The four major classes are schphonzoans(jellyfish), anthazaone(sea anemone, coral), hydrozoans(hydra), and cubozoans(box jelly). Flatworms(phylum platyhelminthes) are simple bilateral animals. They have a solid body and incomplete or absent gut. Many of them are parasitic. The three main classes are planarians, flukes, and tape worms. Phylum molluska are very diverse. They have a complete digestive tract with a mouth and an anus. They have a radulus for feeding, a mantle(epidermus form), and a clenidia(respiratory organ). The three main classes are bastropods(snails, slugs), bivalves(clams, oysters, and mussels), and cephalopods(octopus, squid, cuttlefish, and nautilus). Phylum annelida have segmented bodies They have a coelum, a fluid filled space completely surrounded by muscles. The three types are earthworms, marine worms, and leeches. Arthropods are very diverse too. They have an exoskeleton (cuticle) made of chitin, jointed appendages, and segmented body parts. They are classified into trilobiles(extinct), crustaceans, chelicerates,insects and myriapods. They have an upper circulatory system and sensory organs. Insects are the dominant arthropods. They have three pairs of legs, a pair of antennae, and a body with a head, thorax, and abdomen. Crustaceans have two distinct sections, cephalothorax and abdomen. They have two pairs of antennae, an exoskeleton, and a cerapace. They have many types such as decapods(lobsters and crabs), barnacles(sessile filter feeders wrapped in a hard shell), and isopods(pill bugs). Echinoderms have radial symmetry, an internal skeleton, a water vascular system, and a complete vascular system. Their five classes include feather star and sea lillies, sea stars, brittle stars and brisket stars, sea urchins, sea biscuits, sand dollars and sea cucumbers.
Chordates all have a notochord, a hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and tails. They are amniotes, have 2 circuits of blood vessels, a pulmonary circuit, a systemic circuit, and a 3 or 4 chambered heart, Agnatha are the jawless fish. They are the first recognizable vertebrates. The two groups are lampreys and hag fish. Fish have gills, fins, a skeleton, and jaws. They have paired fins and have gills to breathe underwater. Thy have a lateral tube system and a sensory system. Condrithyes are fish with skeletons made up of cartilage. They must move to breathe. These include catfish, sharks, rays, and skates. Coticythes are bony fish. Lobe finned fish are paired pectonles and pelvic fins that are round in shape and are supported by a single bone. Amphibians evolved from lobe finned fish. They were the first animals with four limbs. They can live in both land and water and can breathe through skin, gills, or lungs. They also lay eggs. They are divided into three groups. Salamanders have a long body, four walking limbs, and a tail. Frogs and toads have glands in their skin that contain poison to ward off predators. Caecillians are legless, burrowing tropical amphibians. Reptiles are ectotherms, covered with dry scales, and have a 3 chambered heart. There are three modern types The first is turtles, tortoises, and terrapods. The second are snakes and lizards. The third are crocodiles and alligators. Birds evolved from theropods. They have hollow bones, fused collar bones, and feathers. Mammals have several characteristics. They have hair to retain heat, mammary glands to provide milk, a middle ear with three bones, and a chewing jaw. There are three types of mammals. Manotremes lay eggs. Marsupials give birth to live young that grow inside a pouch. Euthrians give birth to live young that have completed fetal development.
 |
| A chordate |
A big part of this unit was about the "What on Earth Evolved?" presentations. We each chose a species to do a presentation on. Overall, it when really well. I could have been a little more practiced though and maybe have included some more information. I learned that memorizing the presentation makes it so much more engaging and better. I will try to apply what I learned from this presentation to my end of the year TED talk.
to find more about my take. That;s all folks :)!






No comments:
Post a Comment